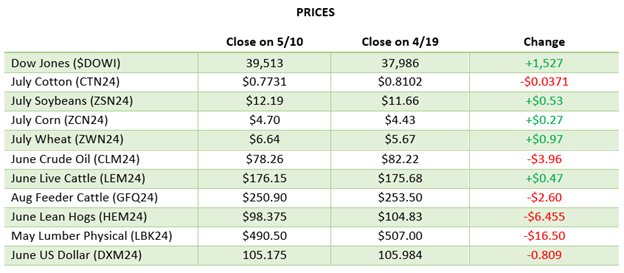
Recap:
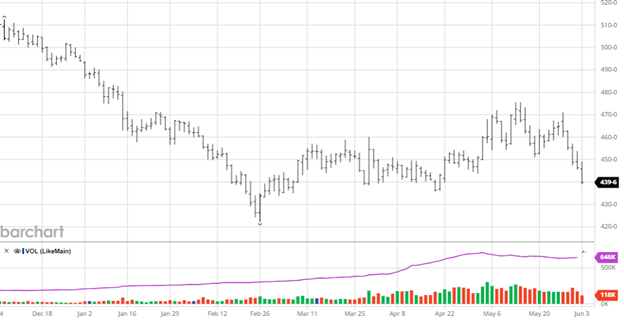
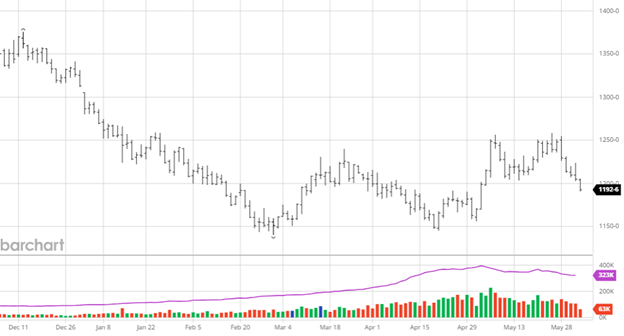
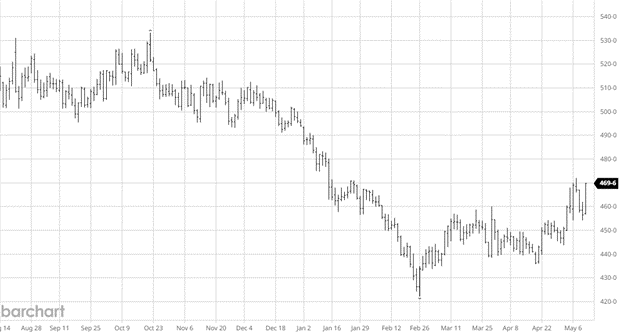
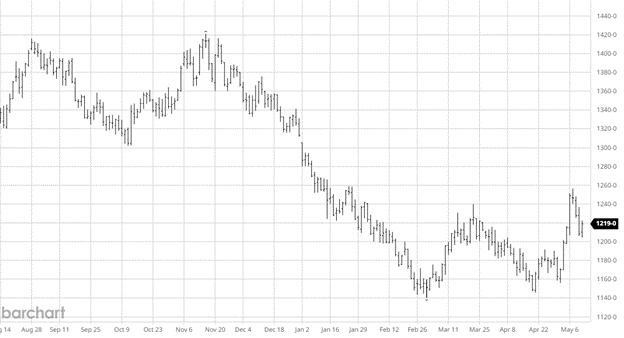
The best word to describe last week’s trade was erosion: erosion in value, erosion in the housing sector, and finally, erosion in the economy. The industry waits for a truckload of sand to show up as the beach slips into the ocean. We searched for green shoots to pop up all week, only to see lower cash prices. One fact remains: it is the lumber market, and rallies are created out of nothing. Last week’s trade indicates the market isn’t ready. Let’s look at a few factors which could already be in play or are forming.
The key factor is the extreme lag of shutdown effects on the market. It indicates a steeper decline in construction than the data shows. With inventory management at a steady pace, sufficient supply is sitting in the pipeline. Last week’s sideways trade was a good indicator. Continued pressure would point to eroding construction.
As housing goes, so goes the economy. Remember that quote? If you have been around long enough, you have seen it occur a few times. This is not a doom-and-gloom forecast. What has happened here is that the industry was geared up for lower rates and didn’t get them. Because of that, today, we see a 9.3-month supply of new homes and confusion about when or if a cut will happen. This doubt will slow construction planning. It won’t slow the plans in place. We can’t underestimate the fall building cycle, but we also can’t underestimate the economic psychology.
If you did a SWOT analysis of our industry, the biggest threat is unemployment. That will kill an already teetering sector. My worry here is that most industries are over-hired. Today, you have a 3-person team doing the work for 2 and a manager who won’t let anyone go. As we have seen in the past, there will be a day when management tells one person to stay and lets the other two go. Today, it is using more to get less. Tomorrow, it will be using less to get more. You don’t have to slow the economy to see this shift. That’s a threat today to housing.
This industry doesn’t have many tailwinds to rely on. China’s weakness continues. Euro and bug kill keep the supply coming despite prices. The fact that Canada shipments increased in the first few months doesn’t help. And finally, our sticky 7%. Most of those reasons are why prices are hitting new lows today. If they remain in place, the market will be forced lower. One constant and a positive is the lumber buyers’ pattern. It’s all in or all out. Not even the algo can figure them out. This last buy round was very guarded, with limited purchases. Most still lost money. It will take time to generate another buy. There is construction every day. It may be less, but it is still going on.
Technical:
The 200-month moving average is 398.47. This has been a support line for the market for many years. It tends to sit very close to breakeven for the mills. It has turned up slightly over the last 10 years, but so has breakeven. I saw in the WSJ an article where the CEO of Weyerhaeuser was quoted as saying producers can’t stay in the red for long. The conversation in the C-suites has changed from so much cash to an all-out panic. When the pig farmers could no longer feed all their pigs it had to cull the herd. Look for a little of that in labor and lumber. FYI: I believe the last time Wall Street wrote an article on lumber; we were at about $1700. from and saw
Daily Bulletin:
https://www.cmegroup.com/daily_bulletin/current/Section23_Lumber_Options.pdf
The Commitment of Traders:
https://www.cftc.gov/dea/futures/other_lf.htm
About the Leonard Report:
The Leonard Lumber Report is a column that focuses on the lumber futures market’s highs and lows and everything else in between. Our very own, Brian Leonard, risk analyst, will provide weekly commentary on the industry’s wood product sectors.
Brian Leonard
bleonard@rcmam.com
312-761-2636






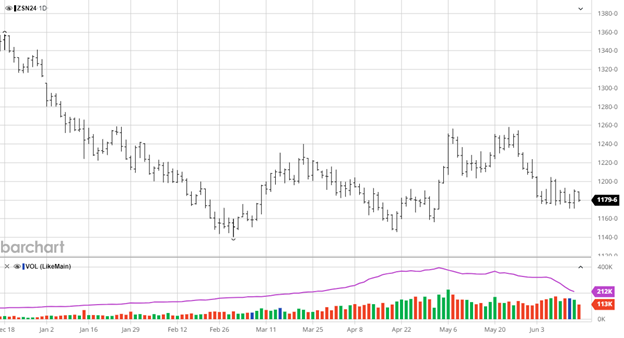
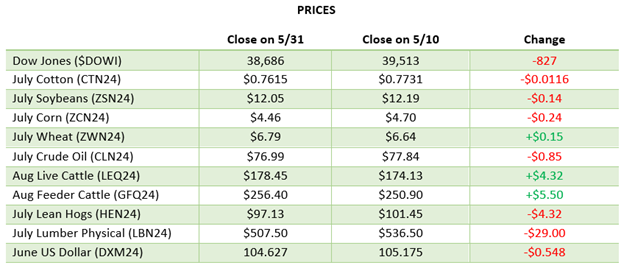
 Beans are lower over the last 2 weeks with them settling into a flat trade this week. The USDA report was uneventful despite the USDA cutting another 1 mmt from Brazil’s bean crop. US exports were revised lower and ending stocks rose as the slow pace of exports continued. With no major surprises and no major weather/production issues yet there is not much bullish news outside of CONAB’s Brazil production estimate which is 207 million bushels below this week’s USDA update.
Beans are lower over the last 2 weeks with them settling into a flat trade this week. The USDA report was uneventful despite the USDA cutting another 1 mmt from Brazil’s bean crop. US exports were revised lower and ending stocks rose as the slow pace of exports continued. With no major surprises and no major weather/production issues yet there is not much bullish news outside of CONAB’s Brazil production estimate which is 207 million bushels below this week’s USDA update.