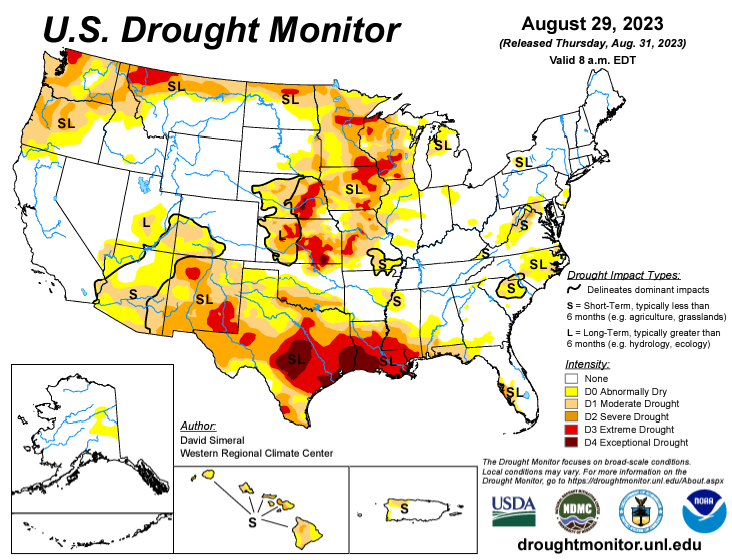
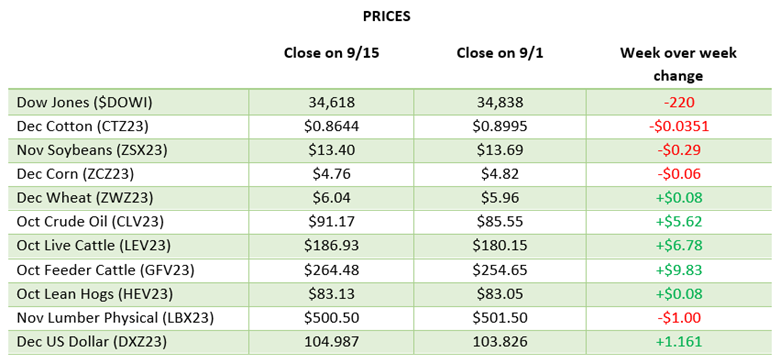
Grain storage has expanded across the country over the last decades as farmers try and time selling to maximize profit potential. While holding the grain until you decide to make a sale is one option, there are several different strategies when it comes to managing the grain. In this short piece we will look at the 4 main strategies and talk about the potential benefits and risks.
1. Hold in bin
As stated above the “sit and hold” method is the most basic and long used method of grain storage. This method makes you long the market as you hope that prices go up from harvest levels over the course of the next year. You are long the market because you will only profit if prices go up, if prices go lower, you miss out on what a sale at harvest could have been.
Here are a few risks that come with this method:
- Price deterioration
- If prices for future months is lower, or moves lower before your sale, you miss out on the price difference between harvest price and sale price. There are numerous factors that can cause this making it your biggest risk.
- Cost of storage
- Running storage bins to keep the quality of the grain at deliverable levels costs money that will cut into the profit potential the longer it is stored.
- Act of God
- While insurance covers AOGs in most situations it is still very much a risk as many farmers face the threat of strong storms and the damage that comes with it.
Now the potential benefits:
- Price appreciation
- The price for future months could go higher, by either improving futures prices or improved basis, and you could potentially profit making a sale at a higher price (minus the extra costs of storage)
- Taxes
- The timing of sales obviously affects your income, meaning there will always be taxes involved. Pay them now or pay them later…Uncle Sam always wins, but if you can write off against income, DO IT.
These are the basic costs and benefits of this method. While this is the most popular method it does carry the risk of prices falling below your breakeven from factors completely out of your control. Now let’s look at the other methods that involve active risk management.
2. Sell and re-own the board
This strategy is for farmers who do not want to store the grain, or do not have the storage, but don’t want to miss out on the potential of higher prices. You can sell the grain to your preferred elevator (lock in a future delivery or current) and buy futures or options to try and take advantage of a price increase. The downside to this is that if the prices move lower, you lose whatever difference is between your sale and the future price.
Examples:
You sell 10,000 bushels of corn for $6.50 Dec contract with +$0.20 basis for a $6.70 sale. You think prices are going to go up over the winter, so you purchase 2 March futures contracts at the current market value of $6.60. Your hunch was correct and March futures goes up to $7.00 and you take profit on your trade by selling them to capture the $0.40 profit minus fees and commissions*. This makes your corn sale equal to $7.10 ($6.50 sale + $0.40 trade profit + $0.20 basis – minus fees and commissions* = $7.10).
Now suppose you were wrong, and prices go down. Using the same information above but prices of the March contract go lower to $6.20. This would result in a loss of $0.40 plus fees and commissions making the value of your corn sale equal to $6.30 – fees and commissions* ($6.50 sale – $0.40 cent trade loss + $0.20 basis – fees and commissions* = $6.30).
*Fees and commissions vary by broker
If the thought of large losses of sales scares people there are other options, such as using options. You can use option trades to limit the capital risk using specific strategies (not all will limit capital risk as some will increase the loss potential). These strategies are not suitable for all investors and each farmer should discuss the risk associated with such trading with their broker or elevator where they offer. For more information on options click here.
3. Sell for delivery in future month
Some farmers will store the grain themselves after selling it for a future delivery month. This strategy is used by farmers when the price difference is worth the cost of storage or they like the futures price but believe basis will improve. Historically, in a “normal market”, the future months will offer some premium to the current month for the crop marketing year. This is because of the risk and unknowns that are present in the market.
Example:
The March contract for corn is trading 15 cents higher than December. If the farmer can store the grain for less than 15 cents leading up to the delivery period, they would consider this sale to capitalize in the margins.
The other way farmers try to maximize selling for future delivery and storage is basis. Elevators change their basis based upon demand in the area. If farmers like the futures price, but no the basis, they may elect this method hoping basis improves.
4. Hold and sell futures against
The final strategy we will discuss is storing grain, while selling futures against it. Farmers will do this if they think the market price is strong, but the basis is poor, or they are unsure of the price direction but do not want to miss out on current levels. This is a way of locking in the futures price on the bushels while allowing time for basis improvement, but not total price risk. If prices move up from when you sell the futures, what you get paid when you decide to sell the physical grain will make up the difference in what your trade lost. On the other side if the price goes down your trade profit makes up for the difference in the cash price come time of sale.
Example:
A farmer believes basis, currently -$0.20, will improve over the next couple months but is happy with a $6.50 price. They sell $6.50 March futures while storing the grain. They were right and basis is flat come February, but the price fell to $6.40. This would result in a final price of $6.50 for the farmer minus fees and commissions ($0.10 trade profit + $0.00 basis + $6.40 cash price – fees and commissions). If they had just made the sale at the time when basis was -$0.20 they would have only received a price of $6.30.
On the other side if prices had gone up to $7.00 and basis had remained at -$0.20 the farmer would receive that $6.30 price minus fees and commissions ($7.00 price at time of sale to elevator -$0.50 loss from trade – $0.20 basis – fees and commissions = $6.30). If they were right about basis and if did improve to $0.00, then the price they would receive is $6.50 minus fees and commissions ($7.00 price from elevator – $0.50 loss from trade + $0.00 basis – fees and commissions).
This is one of the more straightforward strategies as it establishes the price of the sale limiting market factors to only effect basis.
While there are many strategies farmers employ with their stored grain, these are the most common. Each farmer faces their own unique challenges in producing a crop but the decisions about when and how to sell effects everyone. There is no cookie cutter plan as one strategy may make more sense for one farmer than another, therefore it is important to have a plan. Knowing your breakeven and having a marketing plan and sticking to it are how farmers can be successful year in and year out.
RCM Ag Services offers customized risk management solutions for both cash markets and forward pricing opportunities through futures and options. Contact one of our risk managers today: https://rcmagservices.com/contact/