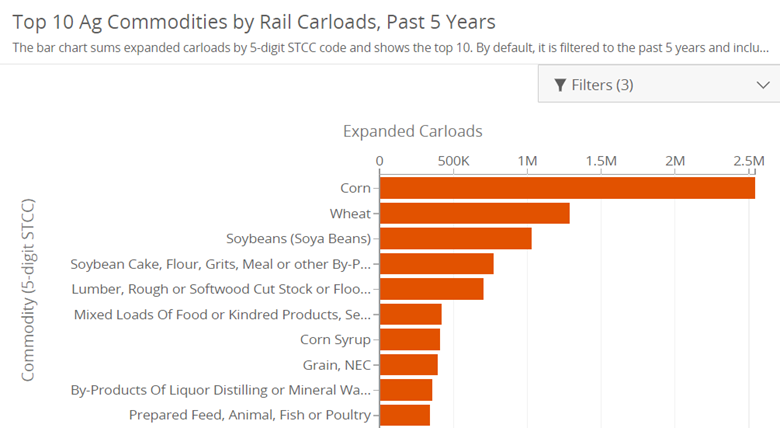
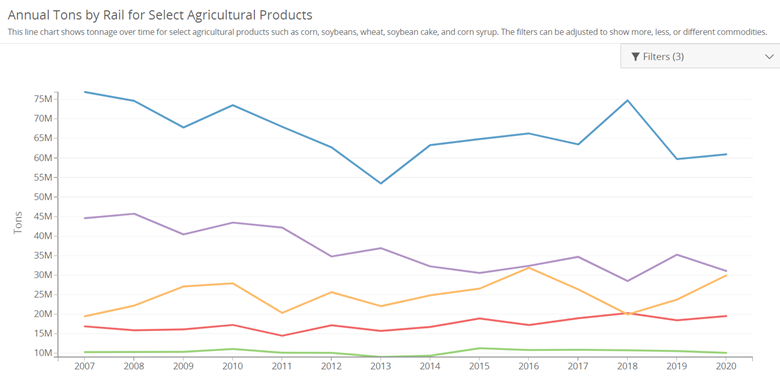
Recently, we had the opportunity to tune in to the captivating podcast episode of @ChiGrl Live Ag Talk on Place Your Trades. The discussion covered various topics impacting the agricultural industry, and we at RCM Ag Services were inspired by the valuable insights shared. Here are our top five takeaways and what they mean for you.
Takeaway 1: Conflict Between EU and Dutch Government: Implications for Farmers
The conflict between the European Union and the Dutch government has significant implications for farmers in the Netherlands. Dutch farmers are vital to the country’s economy and food production, but they face challenges due to the EU’s regulations aimed at environmental sustainability, food safety, and fair competition.
Farmers are concerned about the financial burden of complying with EU regulations, which can require investments in technology and training. This can increase costs and impact their profitability. Compliance may also restrict their autonomy and traditional farming methods.
The conflict raises questions about the competitiveness of Dutch farmers within the EU market. Protecting and supporting farmers could be seen as creating unfair advantages, while prioritizing EU compliance may risk their economic viability.
To address these concerns, constructive dialogue between the EU and the Dutch government is necessary. Government support through financial assistance, incentives, and technical guidance can help farmers transition to more sustainable practices. Finding a balance between sustainable farming and farmers’ economic well-being is crucial.
Takeaway 2: Germany’s Ambitious Organic Farming Goal: A Sustainable Approach
To truly comprehend the implications of Germany’s ambitious plan to reach 30% organic farming by 2030, it is essential to delve into the multifaceted elements contributing to its success. Central to this exploration is an understanding of the role played by government support, incentives, and infrastructure in realizing this transformative vision.
Government support is a crucial driver in facilitating the transition to organic farming.
By examining the effectiveness of existing programs, we can gain insights into the policies and initiatives put in place to encourage farmers to adopt organic practices. This analysis can shed light on the financial and technical assistance provided to farmers, such as grants, subsidies, and access to expertise and resources. Understanding the extent of government support allows us to gauge the magnitude of the commitment and the resources allocated to facilitate this transition.
Incentives are also pivotal in motivating farmers to embrace organic farming methods. By investigating the range of incentives available, such as premium pricing for organic produce, tax incentives, and preferential market access, we can assess their effectiveness in encouraging farmers to switch. Exploring the incentives landscape helps us gauge the level of support and recognition organic farmers receive, influencing their decision to adopt organic practices.
Infrastructure development is another critical aspect that underpins the successful implementation of Germany’s organic farming goal. Establishing robust markets and distribution networks for organic products is essential to ensure a steady demand and supply chain. Analyzing the development of these networks, including the involvement of retailers, processors, and certification bodies, provides insights into the growth potential of the organic market. Understanding how the infrastructure is evolving enables us to identify potential gaps or areas that require further development to support the expansion of organic farming.
By unraveling these key aspects—government support, incentives, and infrastructure—we gain valuable insights into Germany’s journey toward cultivating a greener and more sustainable agricultural landscape. This holistic examination allows us to appreciate the challenges, opportunities, and potential pathways for success in achieving the ambitious target of 30% organic farming. It also offers valuable lessons and inspiration for other countries and stakeholders looking to foster sustainable agricultural practices and contribute to a more environmentally conscious future.
Takeaway 3: Reducing Methane in Farming: Goals and Strategies
The United States is committed to addressing methane emissions in farming to fight climate change. However, there are challenges farmers face in adopting methane reduction technologies.
One challenge is the cost, as these technologies require significant investments in equipment and infrastructure. This can be particularly burdensome for smaller-scale and resource-constrained farms. Lack of financial resources makes it difficult for farmers to adopt these technologies, despite recognizing their environmental benefits.
Another challenge is the technical requirements and maintenance of methane reduction systems. Farmers need to understand the technology and its installation, operation, and upkeep. However, specialized knowledge and training may not always be accessible. Regular maintenance and troubleshooting can also be challenging for farmers with limited technical expertise or resources.
To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to explore the economic and environmental benefits of methane reduction in farming. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and air pollution. By reducing methane emissions, farmers can improve air quality and save costs in the long run by improving operational efficiency.
Government policies and support are essential for widespread adoption of methane reduction practices. Financial incentives like grants or subsidies can assist farmers in implementing methane capture and mitigation systems. Technical assistance programs and knowledge-sharing platforms are vital in helping farmers navigate the complexities of adopting these technologies.
Evaluating existing policies and support mechanisms is important to identify successful strategies and areas for improvement. By studying the effectiveness of current initiatives, policymakers can refine their approaches and develop targeted solutions. Collaboration among government agencies, agricultural organizations, and researchers can foster innovation and develop best practices for methane reduction in farming.
Takeaway 4: Government Support for Biofuels: Impact on Agriculture and Energy Sectors
Governments in Canada and the United States are actively promoting biofuels as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks associated with these renewable fuels to gain a comprehensive understanding of this government push.
Biofuels offer environmental and energy security benefits. They can reduce greenhouse gas emissions since they are derived from renewable sources that absorb carbon dioxide during their growth. When biofuels are burned, they release roughly the same amount of carbon dioxide absorbed during production, resulting in a near-neutral impact on emissions. Replacing fossil fuels with biofuels can make significant progress in mitigating climate change.
Biofuels also have the potential to decrease dependence on imported fossil fuels. Producing biofuels domestically using local feedstocks enhances energy security by reducing reliance on foreign oil and gas. This can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and benefit rural areas where feedstocks are produced.
However, it’s important to address potential drawbacks and challenges. Competition for agricultural land is a concern, as biofuel production requires significant land use. This can lead to conflicts between biofuel feedstock crops and food crops. Careful management is necessary to balance biofuel and food production, avoiding deforestation and biodiversity decline while ensuring food security.
Water usage is another consideration, as some biofuel feedstocks require substantial amounts of water. Expanding biofuel production could strain water resources and exacerbate water scarcity. Sustainable water management practices and water-efficient feedstocks are important to mitigate these concerns.
The potential impact on food prices is a valid concern as well. If biofuel feedstocks compete with food crops, it can affect food availability and affordability, especially for vulnerable populations. Policies should ensure that biofuel production doesn’t negatively impact food security.
To promote the biofuel industry’s growth and viability, innovation is crucial. Research and development efforts focus on improving feedstock development, including non-food crops and algae, to reduce competition with food crops and increase yields. Advancements in processing technologies can also contribute to sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Continued investment in research, along with supportive policies and incentives, can drive further innovation in the biofuel sector.
Takeaway 5: Technology’s Role in Future Farming: Precision, Automation, and Sustainability
The episode highlighted technology’s crucial role in shaping the future of farming. Integrating technology into farming practices comes with challenges and barriers that need to be understood.
One challenge is the cost of adopting farming technology. Precision agriculture tools and automated systems require significant upfront investments. Farmers must assess the long-term benefits against the initial costs and ensure the financial feasibility of implementing these technologies.
Accessibility is another consideration. Not all farmers have equal access to technology, especially in rural or developing areas. Addressing infrastructure, connectivity, and technological literacy issues is important to ensure inclusive technology adoption that benefits all farmers.
Proper training and support are crucial for successful technology integration. Farmers need to acquire the skills and knowledge to effectively use and maintain the technology they adopt. Training programs and workshops can bridge the knowledge gap and empower farmers in utilizing available technological tools.
Ongoing technical support is vital to address any implementation or operational challenges that may arise. Access to reliable assistance and troubleshooting resources ensures a smooth transition and minimizes disruptions to farming operations.
Precision agriculture techniques, automation, and artificial intelligence applications offer benefits such as optimized resource use, improved yields, and reduced environmental impacts. Real-time monitoring, disease management, efficient irrigation, and waste reduction are some of the advantages technology brings to the agricultural industry. By harnessing technology, farmers can enhance profitability while reducing their environmental footprint.
Supporting Farmers and Industry Professionals in the Ever-Evolving Agricultural Sector: Discover the Expertise and Tailored Solutions of RCM Ag Services
RCM Ag Services is committed to supporting farmers and industry professionals navigate these complex agricultural landscapes. Our team of experts is well-versed in the latest trends, regulations, and technologies impacting the industry. We provide various services, including consulting, risk management, and financial solutions tailored to your specific needs.
If you’d like to learn more about how RCM Ag Services can assist you in optimizing your operations and staying ahead in the dynamic agricultural sector, schedule a call with our team here. Together, we can explore strategies to help you thrive in an ever-evolving industry.
Don’t forget to check out the full episode of @ChiGrl Live Ag Talk on Place Your Trade for an in-depth discussion on these critical agricultural topics. You can find the episode on their Twitter page here: https://twitter.com/i/spaces/1YpJkgQAVrwJj?s=20