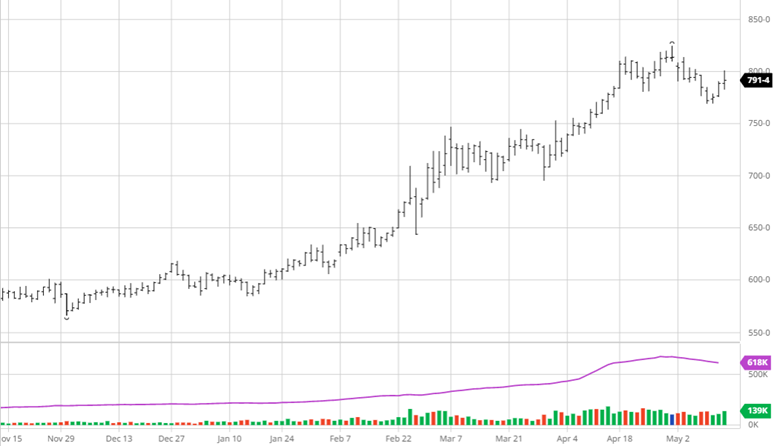
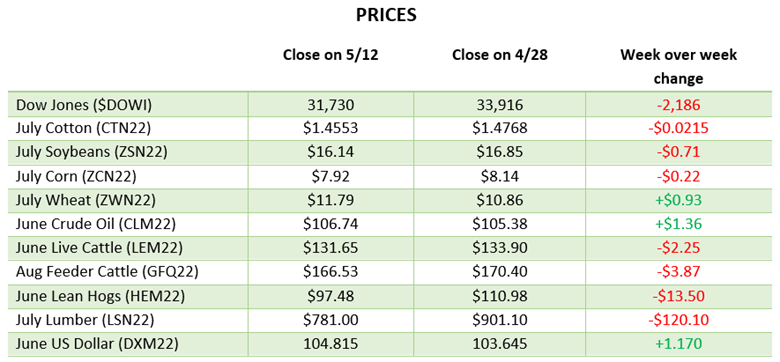
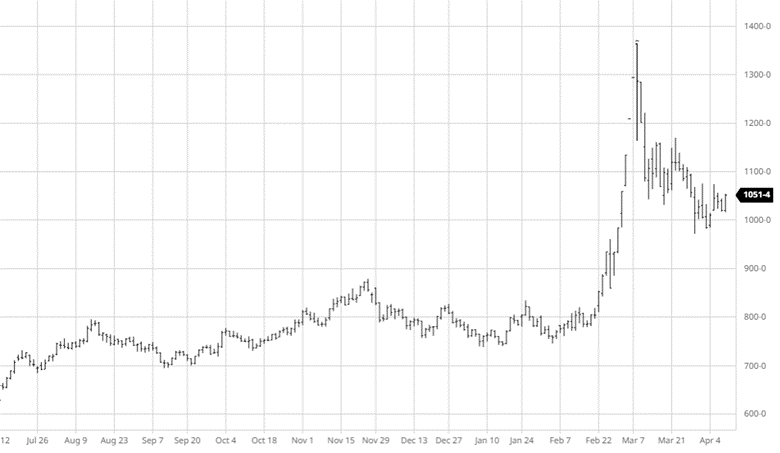
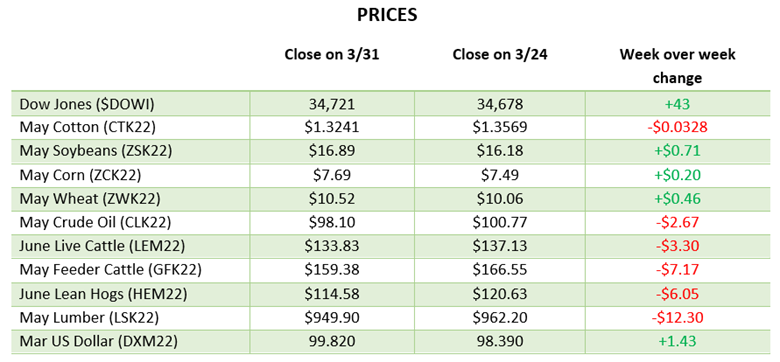
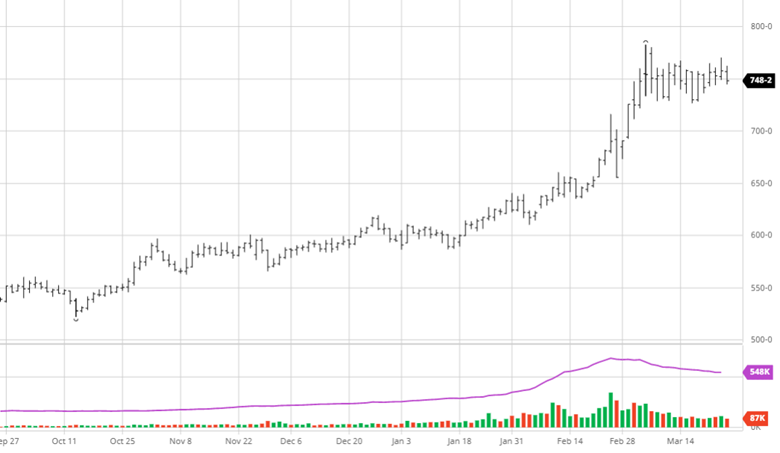
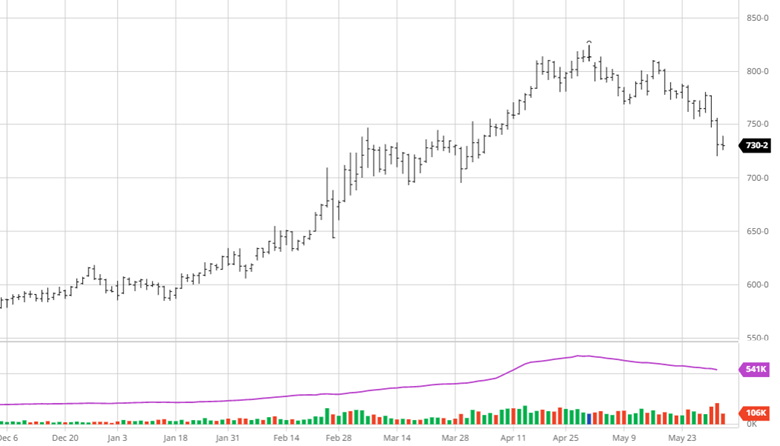
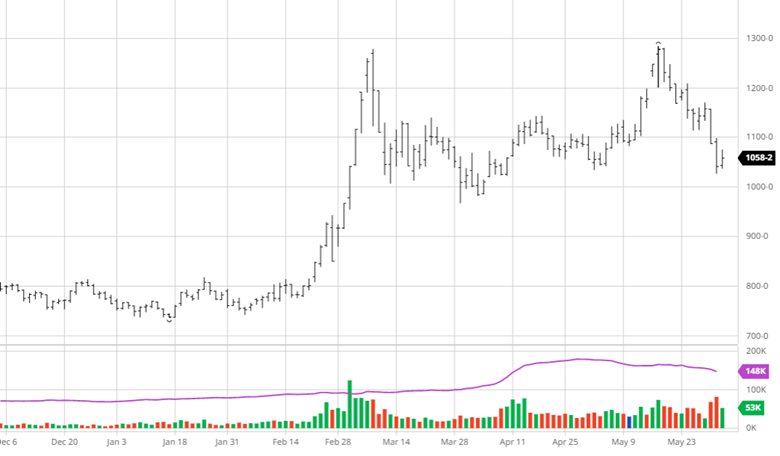
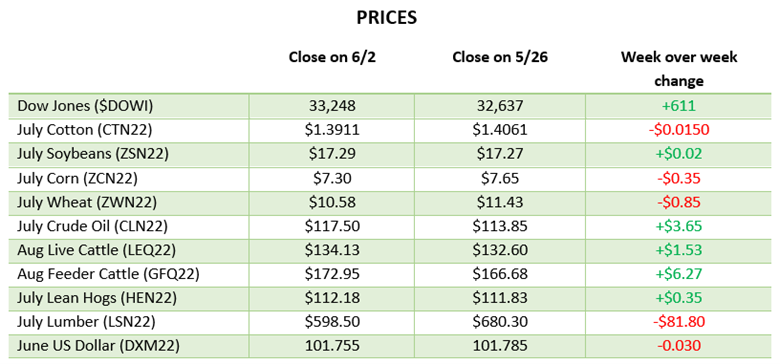
Corn had another tough week with a couple big down days before a quiet day on Thursday. The big news this week was the rumors of talks between Russia and Turkey to discuss a safe trade passage for Ukraine to export grain. While this would be a positive for the world supply, rumors are rumors until something comes to fruition and Russia supposedly would only let that happen if they were to get economic sanctions lifted. Along with this news, corn planting was 86% complete at the start of the week following the long weekend after a few weeks of much needed catch up after the slow start. This is close to the average as parts of North Dakota and Minnesota remain slow due to weather. Eyes will now turn to the weather for this summer while keeping an eye on any further Russia and Ukraine developments.

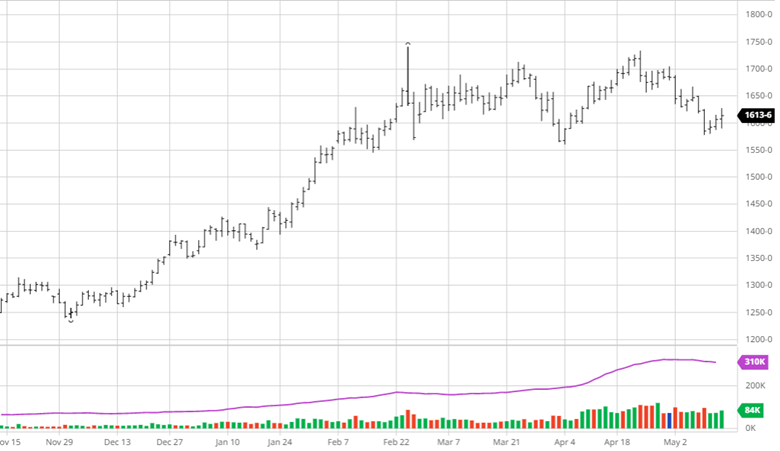
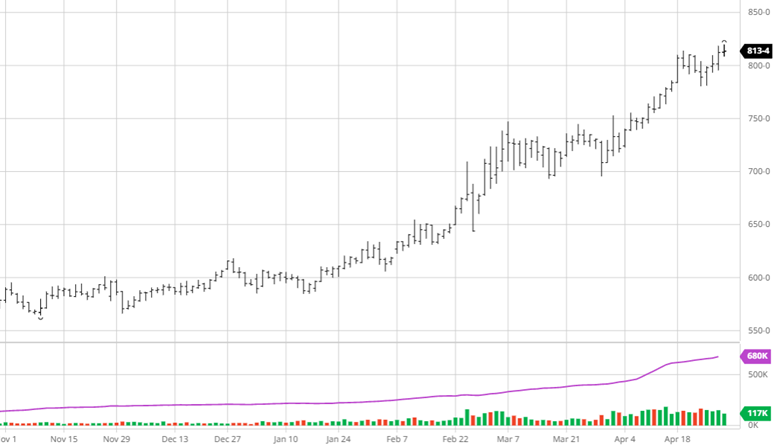
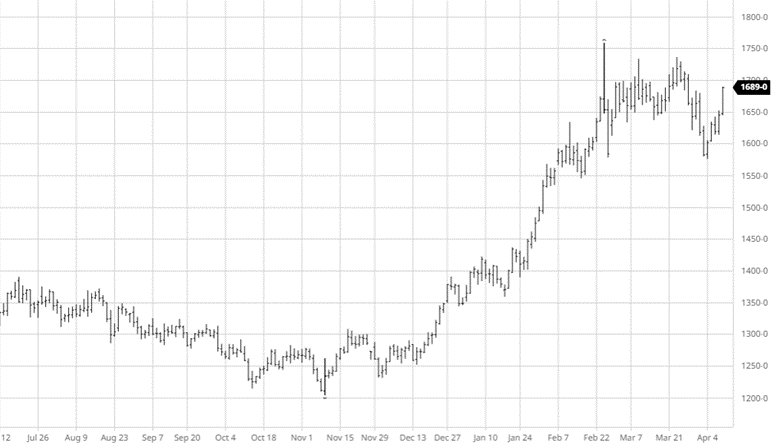
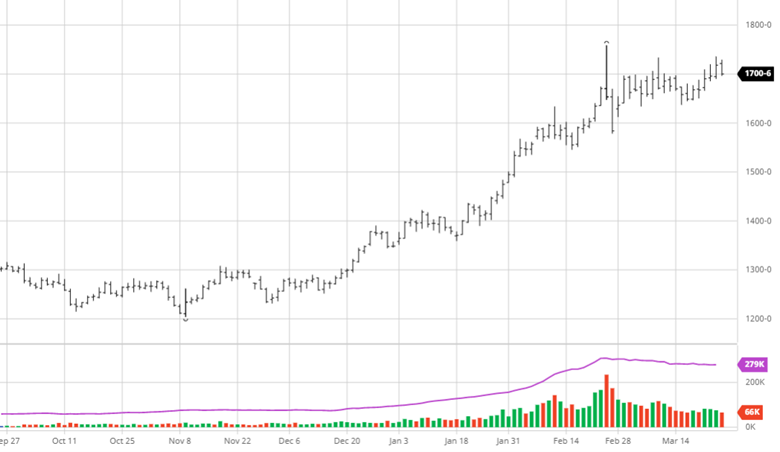
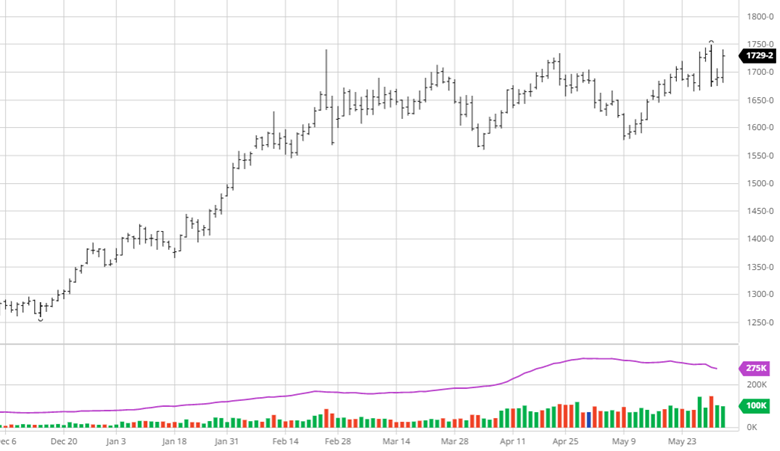
Soybeans have not seen the move down that corn and wheat have the last couple of weeks. Demand for beans remains high across many areas with meal and oil prices moving higher too. 908 million pounds of soybean oil were used to make biofuels in March, the second highest monthly total on record. Exports remain good and with July trading at a 70-cent premium to August the demand has been strong and could be interesting to see if purchases begin for coming months. Soybean planting was 66% complete to start the week, right on the average for this time of year.

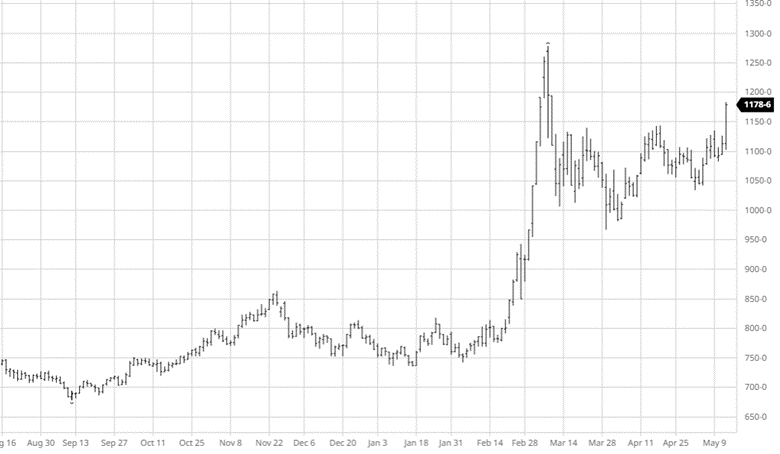
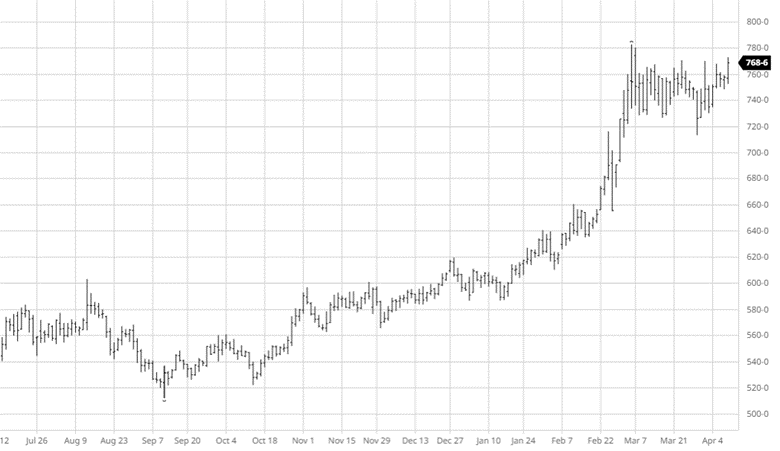
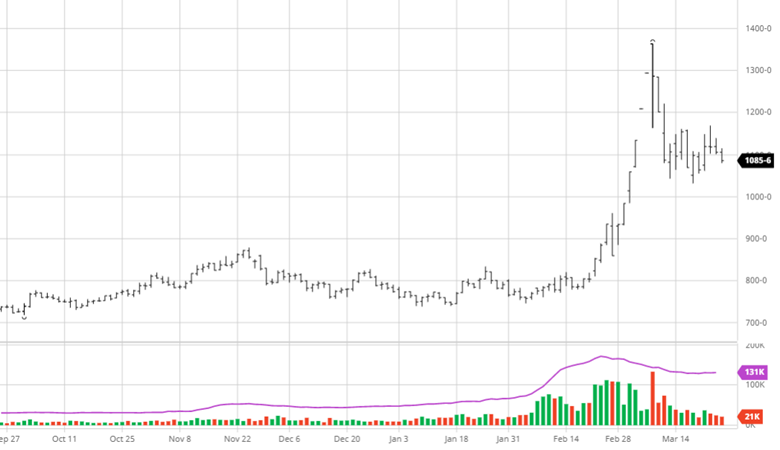
Wheat fell this week on similar news to corn with the rumors of Ukraine being able to export grain. With Ukraine growing more wheat than expected, this will help the world supply if they are able to export some of it. Spring wheat planting was 73% complete to start the week, while this is well below the average the progress made was much needed. Wheat will keep an eye on planting to finish up in areas that dry out and keep an eye on Russia and Turkey discussions.

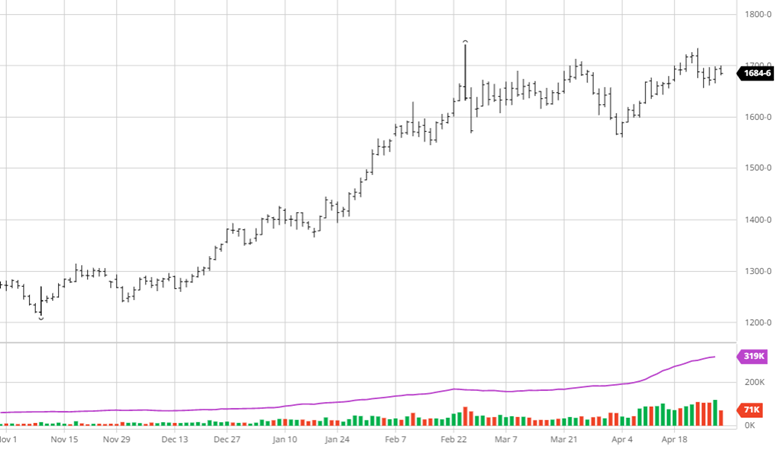
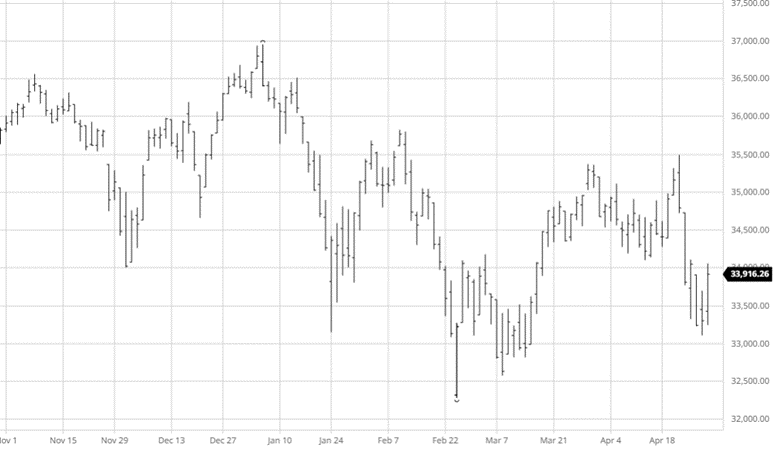
Equity Markets
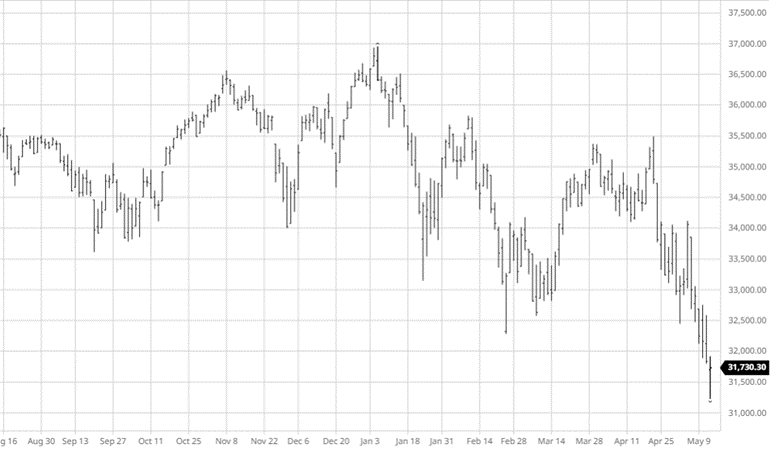
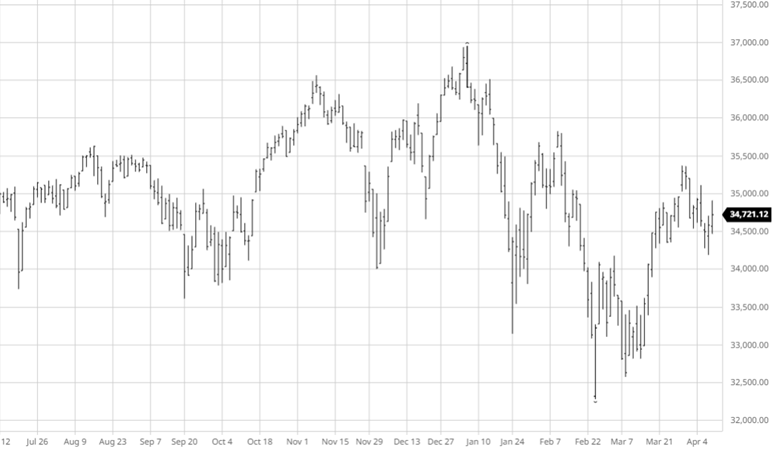
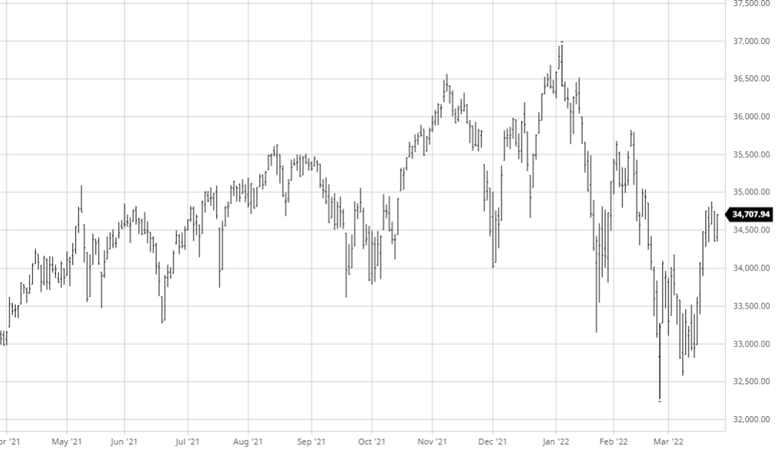
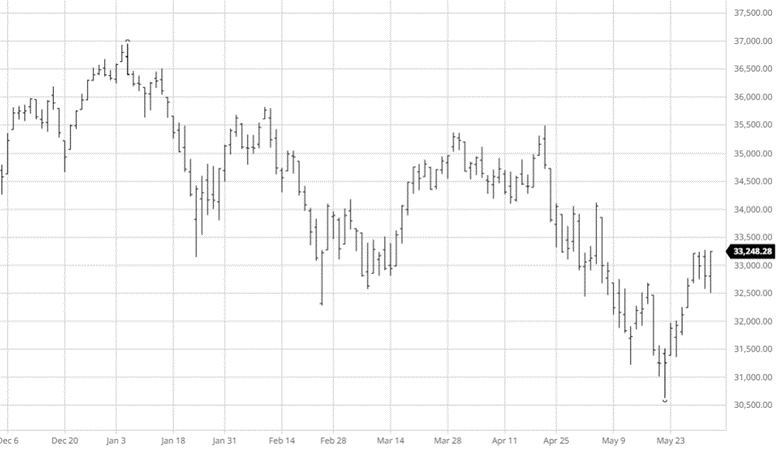
The equity markets have had a good past few days continuing its move higher from the lows from a few weeks ago. The weaker than expected economic data may ease inflation and possibly keep the Fed from being too aggressive in tightening. While the Fed was slow to move on rates the debate about how fast they need to move higher from here continues.
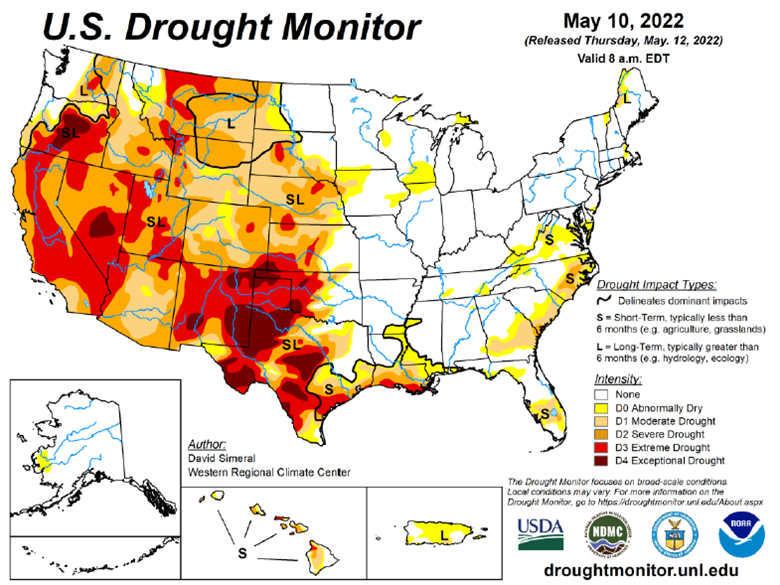
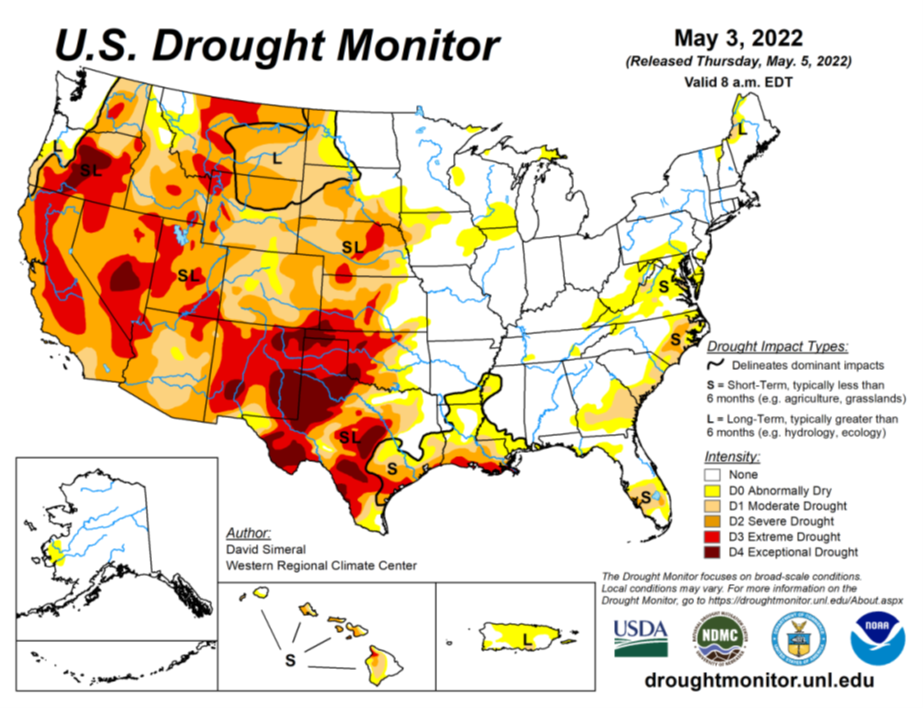
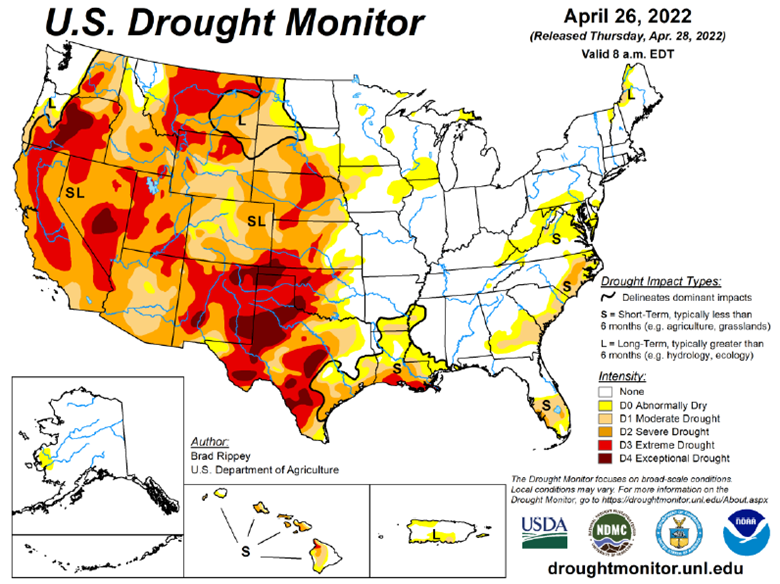
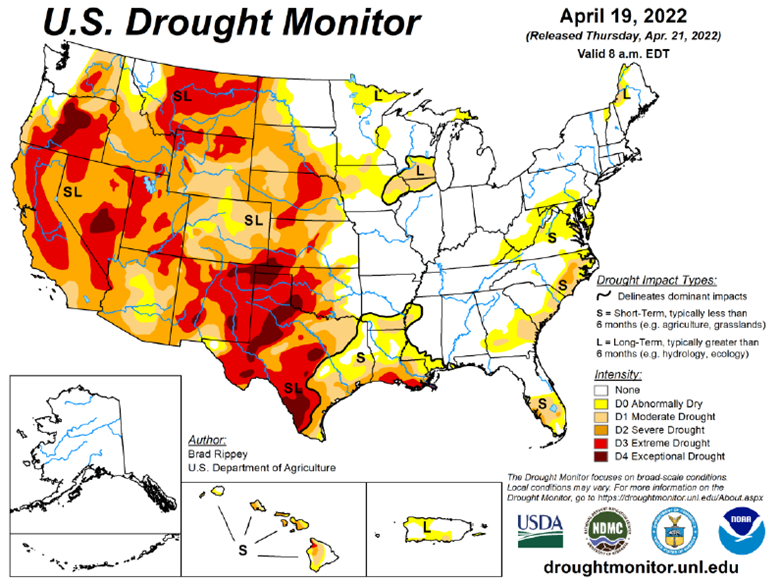
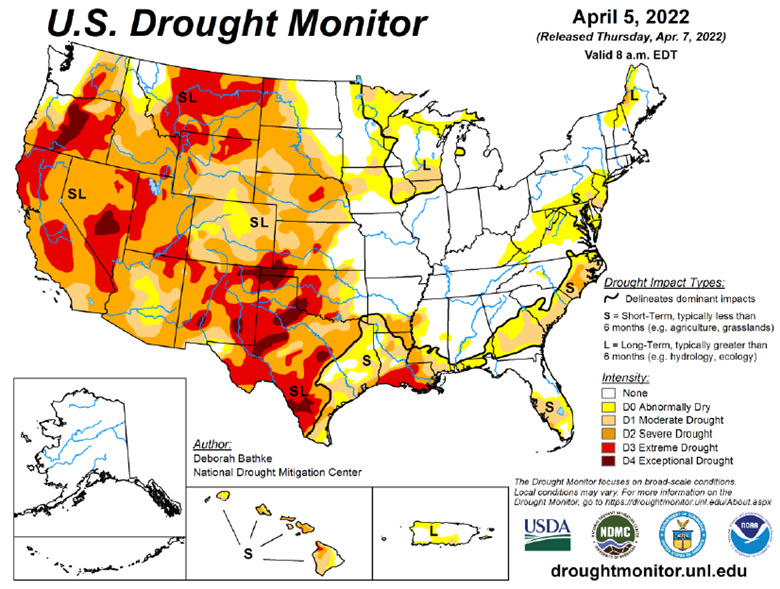
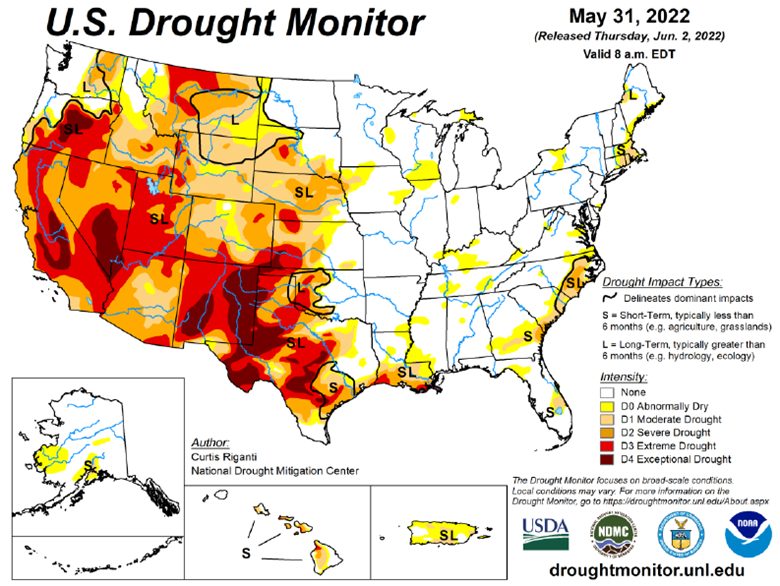
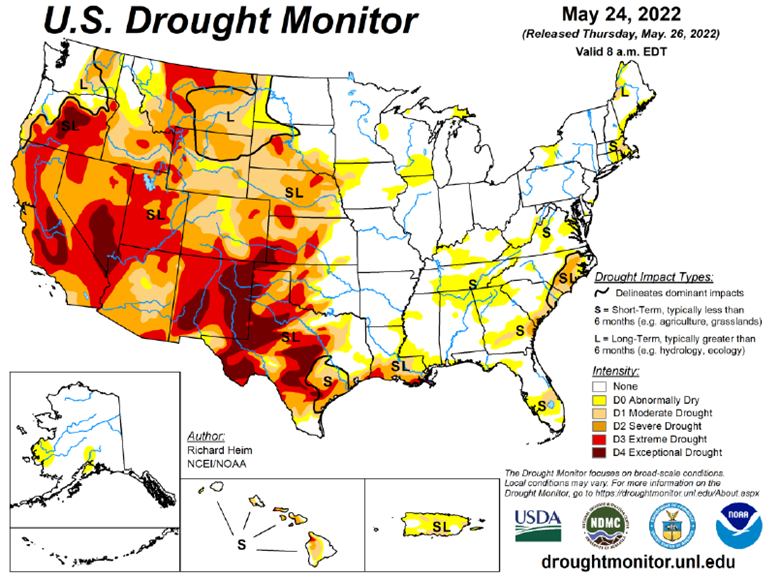
Drought Monitor
The drought monitor below shows where we stand week to week.
Podcast
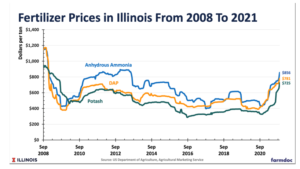
There is an agriculture tug of war happening across the nation, impacting America’s farmland. Fertilizer prices are continuously fluctuating, and it has us taking a page the “The Clash” should we stay, or should we go?! And we aren’t the only ones. Many farmers are asking their agronomist and chemical salespeople, “what will fertilizer cost me the rest of the season, and what are my options if I don’t want to go all-in on my typical fertilizer treatment plan?”
In this episode of the Hedged Edge, we are joined by a special guest who needs no introduction in his local circle, Dick Stiltz. Dick is a 50-year veteran of the fertilizer and chemical industry and is the current Agronomy Marketing Manager of Procurement fertilizer and crop protection at Prairieland FS, Inc in Jacksonville, IL. He is at the pulse of the current struggle and here to discuss the topic at hand.
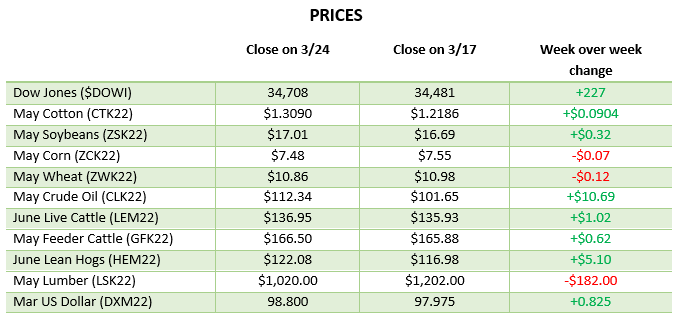
Via Barchart.com
Contact an Ag Specialist Today
Whether you’re a producer, end-user, commercial operator, RCM AG Services helps protect revenues and control costs through its suite of hedging tools and network of buyers/sellers — Contact Ag Specialist Brady Lawrence today at 312-858-4049 or [email protected].